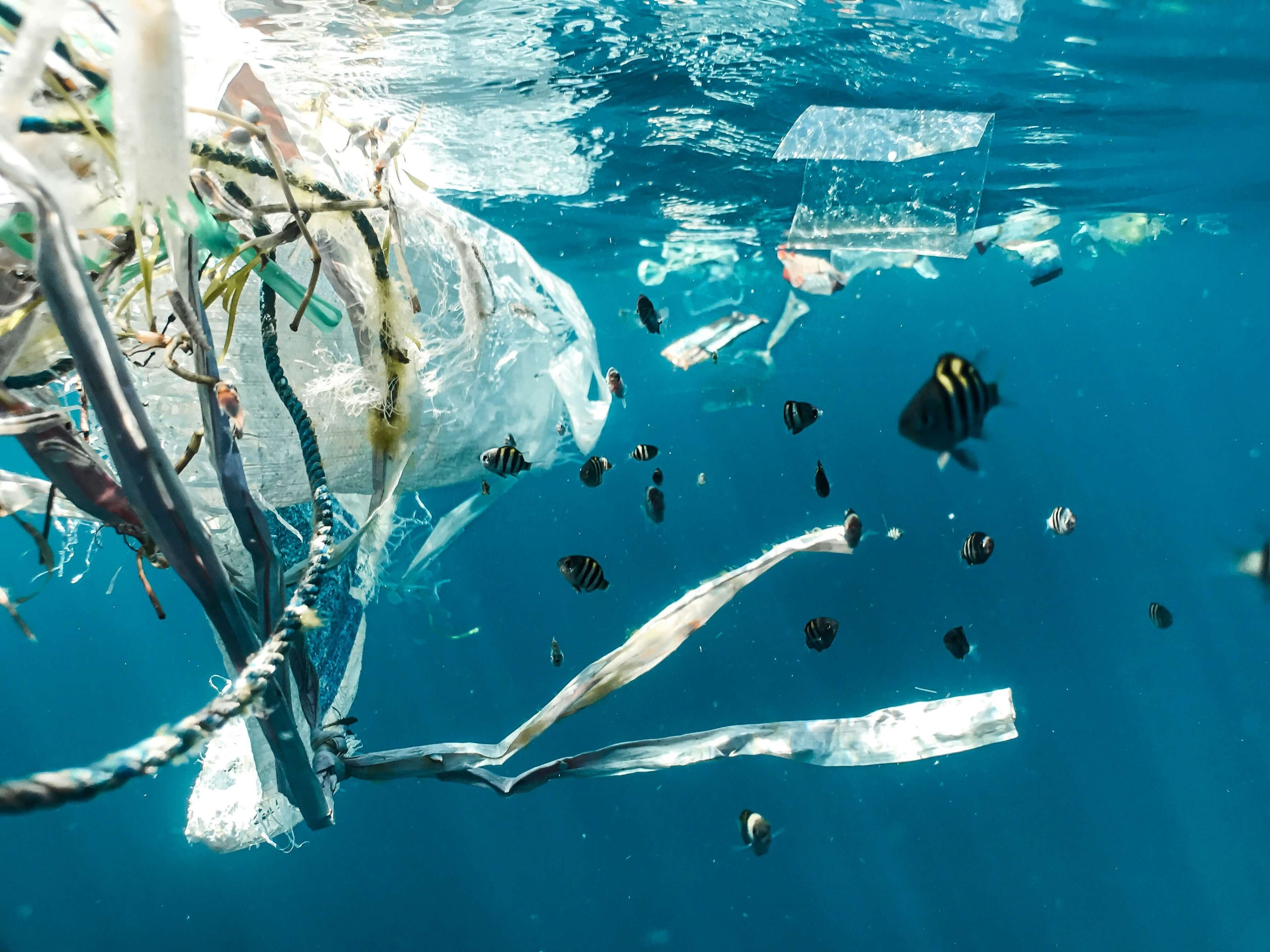
When a sea turtle ingests plastic, it’s not just harmful toxins that put it at risk. Because plastic is impossible to digest, the sea turtle might mistakenly believe it is full. If so, it will stop hunting and starve to death.
The same fate befalls seabird species, 60 percent of whom scientists believe have ingested plastic (Pew Trusts, 2018). This figure is predicted to grow to 99 percent by 2050. And in the 30-odd seconds it’s taken you to read this article so far, half a million single-use plastic bottles have been purchased worldwide (UNEP, 2024).
Rebo’s reusable water bottle collects plastic waste from the oceans
Avoiding single-use plastic bottles by opting for reusable water bottles is an obvious way to reduce plastic waste and mitigate the impact on our oceans. Startup Rebo has a solution that goes a step further. Their reusable water bottle connects to an app, and for every bottle of water you drink, the company removes a plastic bottle from the beach via their partner, Parley for the Oceans. The app also shows users nearby water refill stations, to make refilling their water bottles more convenient.
Reusable water bottles may not be as sustainable as we think
Rebo’s bottle is certainly a great innovation. But, before you think about adding their bottle to your online basket and doing your bit to save the oceans, first consider the reusable water bottle you likely already own. These bottles have become a marker of sustainability in recent years, with green-focused events giving them away as freebies and brands marketing them as an essential purchase–or the ultimate gift–for climate-conscious consumers. As of 2023, 60 percent of people in the UK use a refillable water bottle, compared to just 20 percent of people in 2015.
While some reusable bottles are made from recycled materials, brands don’t need sustainable production practices to claim environmental credentials. The promise of a greener lifestyle is built into the product itself, marketed by brands conjuring images of sea life whose stomachs are filled with plastic.
There are drawbacks to reusable water bottles being on-trend
At first, the rise in sales of the Stanley Cup didn’t seem like a bad thing. The growing prevalence of this reusable stainless steel drinking cup seemed to indicate sustainable values had gone mainstream. But at some point, things started spiralling. Stanley Cup enthusiasts began purchasing the product in multiple colours. If you’re wondering at what point owning multiple reusable drinking cups stops being good for the environment and crosses the line into plain consumerism, stop before you get to 103, which is how many North Carolina-based Mariana Conti Schwarz owns.
And if you need any further indication that owning the Stanley is more of a status symbol than an act of environmental activism, you just need to look at the images of shoppers pushing one another over in their attempts to get their hands on limited-edition releases.
Where do we go from here – and what do we drink from?
The concept of the Rebo water bottle is undoubtedly positive, and their collaboration with a beach cleanup project is a great way to help consumers maximise the ocean-saving impact of their reusable water bottle purchase.
But the most environmentally friendly water bottle is undoubtedly the one you already own. If you want to check where to refill your bottle, you don’t necessarily need a Rebo bottle: Refill is an app that shows water refill locations globally.
Before you buy the latest technology that promises to revolutionise a process that humans have been doing for hundreds of thousands of years, just grab the nearest bottle you have lying around, fill it up, and take a drink.